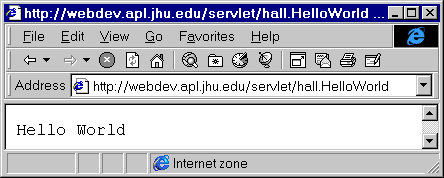
| First Servlets |
|---|
GET requests.
GET requests, for those unfamiliar with HTTP,
are requests made by browsers when the user
types in a URL on the address line, follows a link from a Web page,
or makes an HTML form that does not specify a METHOD. Servlets can also
very easily handle POST requests, which are generated when someone creates
an HTML form that specifies METHOD="POST". We'll discuss
that in later sections.
import java.io.*;
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.http.*;
public class SomeServlet extends HttpServlet {
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
// Use "request" to read incoming HTTP headers (e.g. cookies)
// and HTML form data (e.g. data the user entered and submitted)
// Use "response" to specify the HTTP response line and headers
// (e.g. specifying the content type, setting cookies).
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
// Use "out" to send content to browser
}
}
(Download template source code -- click
with the right mouse on the link or hold down SHIFT while clicking on the link.)
To be a servlet, a class should extend
HttpServlet
and override doGet or doPost (or both), depending
on whether the data is being sent by GET or by POST. These methods
take two arguments: an
HttpServletRequest and an
HttpServletResponse.
The HttpServletRequest has methods that let you
find out about incoming information such as FORM data, HTTP request headers,
and the like. The HttpServletResponse has methods that
lets you specify the HTTP response line (200, 404, etc.),
response headers (Content-Type, Set-Cookie, etc.),
and, most importantly, lets you obtain a
PrintWriter used to
send output back to the client. For simple servlets, most of the effort is
spent in println statements that generate the desired page.
Note that doGet and doPost throw two exceptions, so you are required
to include them in the declaration. Also note that you have to import classes in
java.io (for PrintWriter, etc.),
javax.servlet (for HttpServlet, etc.),
and javax.servlet.http (for HttpServletRequest and
HttpServletResponse). Finally, note that
doGet and doPost are called by the service method,
and sometimes you may want to override service directly, e.g.
for a servlet that handles both GET and POST request.
package hall;
import java.io.*;
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.http.*;
public class HelloWorld extends HttpServlet {
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
out.println("Hello World");
}
}
servlets in the JWS installation
hierarchy. However, I placed this servlet in a separate package (hall) to avoid
conflicts with other servlets on this server; you'll want to do the same
if you are using a Web server that is used by other people and doesn't have
a good infrastructure for "virtual servers" to prevent these conflicts automatically. Thus,
HelloWorld.java actually goes in a subdirectory called hall in the
servlets directory. Note that setup on most other servers is similar,
and the servlet and JSP examples in the tutorial have also been tested
using BEA WebLogic and IBM WebSphere 3.0. WebSphere has an excellent mechanism for virtual
servers, and it is not necessary to use packages solely to prevent name conflicts
with other users.
If you've never used packages before, there are two main ways to compile classes that are in packages.
One way is to set your CLASSPATH to point to the directory above
the one actually containing your servlets. You can them compile
normally from within the directory. For example, if your base directory is
C:\JavaWebServer\servlets and your package name (and thus
subdirectory name) is hall, and you
were on Windows, you'd do:
DOS> set CLASSPATH=C:\JavaWebServer\servlets;%CLASSPATH%
The first part, setting the
DOS> cd C:\JavaWebServer\servlets\hall
DOS> javac YourServlet.java
CLASSPATH, you probably want to do permanently,
rather than each time you start a new DOS window. On Windows 95/98 you'd typically put
the "set CLASSPATH=..." statement in
your autoexec.bat file somewhere after the line that set
the CLASSPATH to point to servlet.jar and jsp.jar.
On Windows NT, you'd go to the Start menu, select Settings, select Control Panel,
select System, select Environment, then enter the variable and value.
Note also that if your package were of the form name1.name2.name3 rather than
simply name1 as here, you'd still have the CLASSPATH point to the top-level
directory of your package hierarchy (the one containing name1).
A second way to compile classes that are in packages is to go to the directory
above the one containing your servlets, and then do
"javac directory\YourServlet.java" (Windows; note the backslash) or
"javac directory/YourServlet.java" (Unix; note the forward slash).
For example, suppose again that your base directory is
C:\JavaWebServer\servlets and your package name (and thus
subdirectory name) is hall, and you
were on Windows. In that case, you'd do the following:
DOS> cd C:\JavaWebServer\servlets
Note that, on Windows, most JDK 1.1 versions of
DOS> javac hall\YourServlet.java
javac
require a backslash, not a forward slash, after the directory name.
This is fixed in JDK 1.2, but since many Web servers are configured to use JDK 1.1,
many servlet authors stick with JDK 1.1 for portability.
Finally, another advanced option is to keep the source code in
a location distinct from the .class files, and use javac's "-d" option to
install them in the location the Web server expects.
servlets directory
within the main JWS installation directory,
and are invoked via http://host/servlet/ServletName. Note that
the directory is servlets, plural, while the
URL refers to servlet,
singular. Since this example was placed in the hall package, it would
be invoked via http://host/servlet/hall.HelloWorld. Other Web
servers may have slightly different conventions on where to install servlets
and how to invoke them. Most servers also let you define aliases for servlets,
so that a servlet can be invoked via http://host/any-path/any-file.html.
The process for doing this is completely server-specific; check your server's
documentation for details.

println statements to build
a legal Web page. The first step is done by setting the
Content-Type response header. In general, headers can be set
via the setHeader method of HttpServletResponse,
but setting the content type is such a common task that there is also a special
setContentType method just for this purpose.
Note that you need to set response headers before
actually returning any of the content via the PrintWriter.
Here's an example:
package hall;
import java.io.*;
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.http.*;
public class HelloWWW extends HttpServlet {
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
response.setContentType("text/html");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
out.println("<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC \"-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.0 " +
"Transitional//EN\">\n" +
"<HTML>\n" +
"<HEAD><TITLE>Hello WWW</TITLE></HEAD>\n" +
"<BODY>\n" +
"<H1>Hello WWW</H1>\n" +
"</BODY></HTML>");
}
}
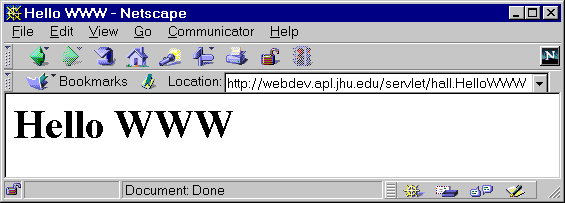
println statements. The
real solution is to use Java Server Pages (JSP), which is discussed
later in this tutorial.
However, for standard servlets, there are two parts of
the Web page (DOCTYPE and HEAD) that are unlikely to
change and thus could benefit from being incorporated into a simple utility file.
The DOCTYPE
line is technically required by the HTML spec, and although most major
browsers ignore it, it is very useful when sending pages to formal
HTML validators.
These validators
compare the HTML syntax of pages against the formal HTML specification,
and use the DOCTYPE line to determine which version of HTML to check
against. Their use is very highly recommended both for static HTML pages and
for pages generated via servlets, so the use of DOCTYPE is well worth
the effort, especially if it can be easily incorporated into a
servlet utilities class.
In many Web pages, the HEAD line contains nothing but the TITLE, although
advanced developers may want to include META tags and style sheets. But
for the simple case, I'll create a method that takes a title as input
and returns the DOCTYPE, HEAD, and
TITLE entries as output. Here's the code:
package hall;
public class ServletUtilities {
public static final String DOCTYPE =
"<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC \"-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.0 Transitional//EN\">";
public static String headWithTitle(String title) {
return(DOCTYPE + "\n" +
"<HTML>\n" +
"<HEAD><TITLE>" + title + "</TITLE></HEAD>\n");
}
// Other utilities will be shown later...
}
package hall;
import java.io.*;
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.http.*;
public class HelloWWW2 extends HttpServlet {
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
response.setContentType("text/html");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
out.println(ServletUtilities.headWithTitle("Hello WWW") +
"<BODY>\n" +
"<H1>Hello WWW</H1>\n" +
"</BODY></HTML>");
}
}